A Comprehensive Comparison of 5G and CBRS Technologies
In the rapidly evolving landscape of wireless communication, two technologies stand out for their potential to revolutionize how we connect and interact with the world: 5G and Citizens Broadband Radio Service (CBRS). This article provides an in-depth analysis of both technologies, comparing their capabilities, applications, and the roles they will play in shaping the future of connectivity.

Understanding 5G Technology
5G technology is the latest iteration in cellular network technology, promising to deliver unprecedented speed, reliability, and flexibility. It is designed to meet the growing demand for data and connectivity in the modern world.
Key Features of 5G
- Enhanced Bandwidth: 5G networks utilize a broad spectrum, including low, mid, and high-frequency bands, allowing for increased data transmission rates.
- Ultra-Low Latency: With latency as low as 1 millisecond, 5G enables real-time communication, essential for applications such as autonomous driving and telemedicine.
- Massive Device Connectivity: 5G can support up to a million devices per square kilometer, facilitating the expansion of the Internet of Things (IoT).
Network Slicing: This feature allows operators to create multiple virtual networks with different qualities of service, tailored to specific needs or applications.
The Impact of 5G
The deployment of 5G networks is set to unleash a new wave of digital transformation. Industries such as healthcare, transportation, and manufacturing stand to benefit significantly from the high-speed, low-latency connectivity that 5G offers. Consumers will experience enhanced mobile broadband, with faster download speeds and seamless streaming services.
Exploring CBRS: The Flexible Spectrum Option
CBRS is a groundbreaking approach to spectrum management that enables efficient use of radio frequencies. It operates in the 3.5 GHz to 3.7 GHz band and is characterized by a three-tiered sharing model.
The Three Tiers of CBRS
- Incumbent Access: Existing users, including government entities, have protected access to the spectrum.
- Priority Access Licenses (PAL): Organizations can purchase licenses for exclusive use in specific geographic areas, ensuring interference-free operation.
- General Authorized Access (GAA): Open to the public, this tier allows anyone to use the spectrum, provided they do not interfere with higher-tier users.
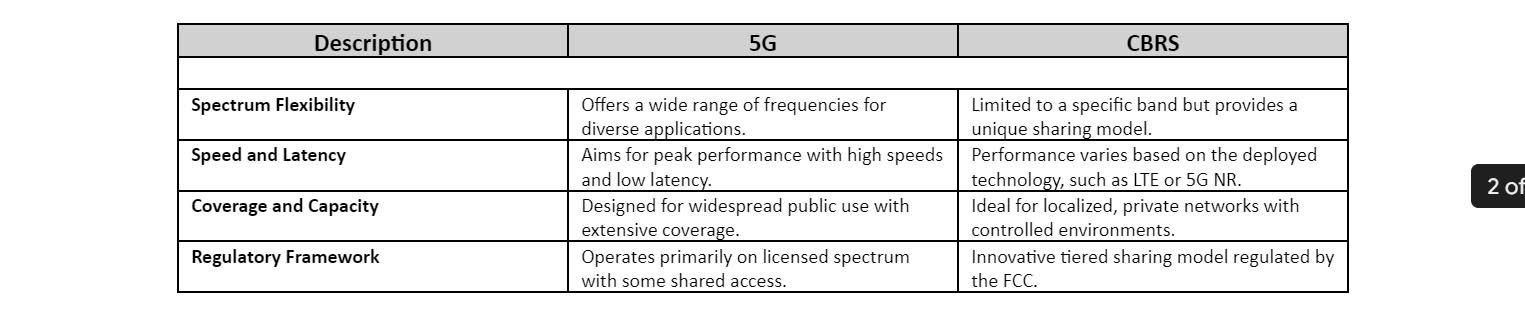
Comparative Analysis: 5G vs. CBRS
While 5G and CBRS are distinct in their spectrum and applications, they are not mutually exclusive. In fact, they can be complementary.
The Synergistic Future of 5G and CBR
Looking ahead, the integration of 5G and CBRS will play a pivotal role in the advancement of wireless communication. 5G’s broad capabilities complemented by CBRS’s flexibility for private network deployment, pave the way for a connected future that is more dynamic and adaptable than ever before.
The Road Ahead
As we embrace these technologies, we can expect a transformation in how we interact with devices, data, and each other. The synergy between 5G and CBRS will enable a plethora of new applications and services, driving innovation and growth across various sectors.
Conclusion
The comparison between 5G and CBRS reveals two technologies with distinct characteristics and applications, both essential for the future of connectivity. Their concurrent development and deployment will undoubtedly lead to a more connected and technologically advanced society.








